Skin Layers Need Protection?
Good results give you beautiful skin!
Let’s first look at the structure of the skin layers.
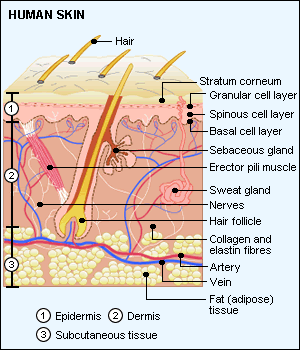
Your skin layers make up the largest organ of your body,
accounting for 12% to 16% body weight and covering about 4 to 6
square meters. It's unique body covering is about 70% water, 25%
protein and 2% lipids.
The remainder includes other substances including trace minerals
and nucleic acids.
Its main job is to form a protective barrier, controlling the
loss of water from body cells and tissues. Without this
protective barrier, your body would quickly dehydrate.
And that's when you start to see all the signs of aging skin.
It consists of 3 layers:
Epidermis, Dermis and Subcutis.
The Epidermis makes up the top layer and is the thinnest
layer of about 1millimetre. It consists of 3 types of cells:
Keratinocyte cells; these cells make the protein
keratin. Kertinocytes are responsible for producing hair,
toenails and fingernails.
Melanocyte cells; these cells produce the pigment
melanin. Melanin provides color, as well as giving protection
from Ultra Violet radiation.
Langerhans cells; these cells form part of the immune
system and intercept foreign substances that try to pass through
its protective structure.
The epidermis itself forms four distinct layers:
Stratum Corneum: this is the top layer and is made from
dead, hard, tough cells that form the hard outer surface.
Stratum germinativium: this forms the 3 lower layers from
bottom to top.
These are the Basal cell layer, the Spinous cell
layer and the Granular cell layer.
One of the functions of these layers is to produce millions of
new cells every day. The new cells form at the bottom of the
epidermis.
The Dermis makes up the second layer and is just below
the Epidermis. It is a thick, supple and sturdy layer and makes
up about 90 percent of the skin's thickness.
The Dermis contains many types of tissues, including blood
vessels, nerves, muscle cells, sweat and sebaceous glands and
hair follicles. It also contains the proteins Collagen and
Elastin,.
The Subcutis is the deepest layer and is made up mainly of fat.
The Subcutis and the subcutaneous layer, manage your the
functions of feeding, excreting and heat exchange.
Adipocytes are the fat cells in this layer.
They have several jobs which include providing energy, serving
as a heat insulator for the body, acting as a shock absorber to
protect tissues underneath and providing resilience.
Sweat glands originate in this layer and excrete waste
matter through perspiration.
Your sweat controls your body's temperature by evaporating and
cooling your skin surface. (That’s why "Goose-bumps" can appear
when the fine layer of muscles found in this layer contract.)
Where Did that Wrinkle Come From?
So Collagen and Elastin are the proteins responsible for the
elasticity, tone and texture.
In young Adults, Collagen and Elastin are abundant, providing
moisture, elasticity and strength.
But over time the amount of these proteins decreases,
causing aging, wrinkles and loss of elasticity.
As the structural support of Collagen breaks down, skin begins
to lose its tone, becoming thinner and eventually susceptible to
sagging.
And as Elastin fibres break down, your outer covering loses its
elasticity, no longer having that “snap back” quality.
So keep your skin layers moisturised with a good Anti Aging Cream or Serum
Return to Best Anti Aging Guide Home Page